Eisen's Blog
在 EasePi ARS2 安装 OpenClash
2022 December-13
最近家里的 EasePi ARS2 系统盘满了,想了想没什么重要的东西直接做了系统重制,作为旁路由第一步就是重装代理,这里简单记录下。
下载 openclash
去 OpenClash 下载 OpenWrt 的客户端,在 Release 也面也包含了安装的依赖。
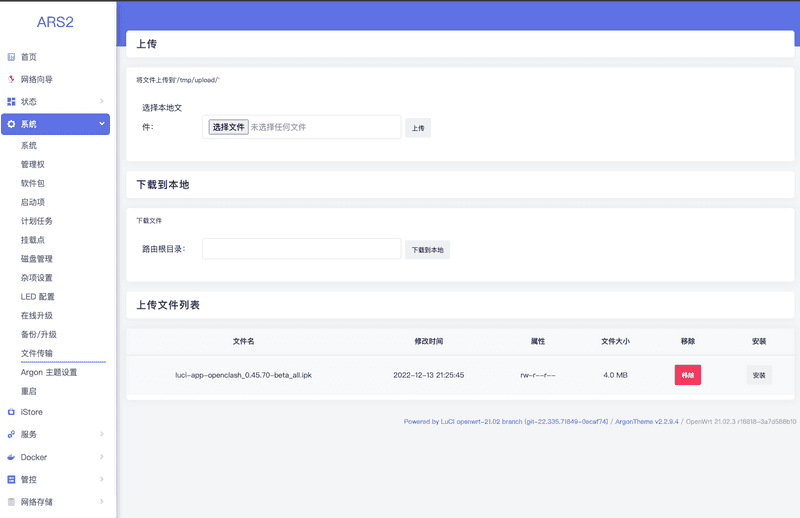
下载之后本来打算用 scp 拷贝过去,但感觉 openwrt 里的这个 ssh 有点不太一样,scp 会失败,最终还是要从页面的「系统」-「文件传输」把下载的安装包传过去。
安装 openclash
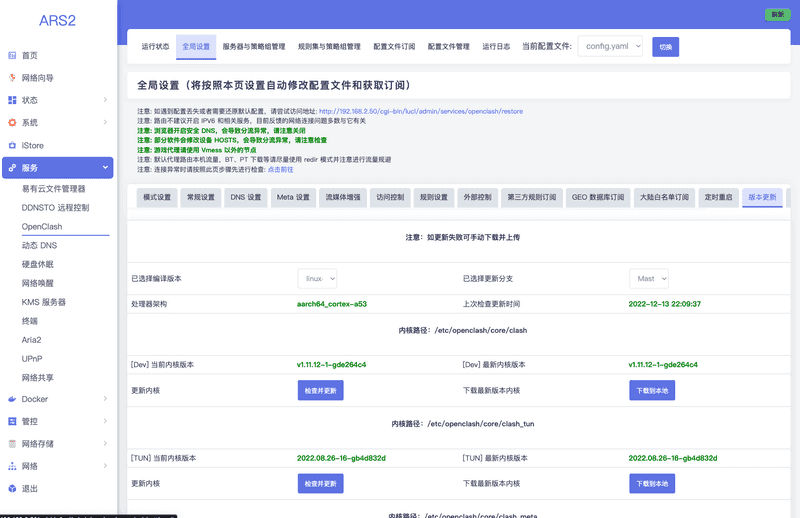
首先安装相应的依赖,然后执行命令 opkg xxx.ipk 就可以了。安装成功之后重新登录 ARS2 的管理页面在左侧导航栏的「服务」下面就会多了「OpenClash」了。下一步按照 OpenClash 版本更新 介绍的更新流程,去「OpenClash」-「全局设置」-「版本更新」这个页面(有点难找),点击下面的「更新内核」,自动下载 clash 内核。
添加配置并启动
下一步就要去「配置文件订阅」更新订阅的代理源了,这里我没办法说的更多了,懂得都懂。最后在「运行状态」标签页滑到最下面点击「启动 OPENCLASH」。
测试
ssh 进去,curl google.com 感受下效果。
后面就可以按照 使用 EasePi ARS2 做旁路由 的流程把这个设备设置成旁路由使用了。
使用 EasePi ARS2 做旁路由
2022 December-10
最近折腾了下那个一直放在家里的 EasePi ARS2 ,把它做成了家里的一个旁路由,这里记录一下。
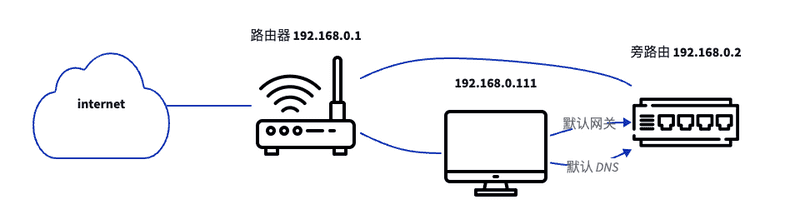
首先这个东西就是一个非常正统的「软路由」了,搞这个东西的基本用法应该就是把它当个路由器直接接管家里网络的三个方面:
- 接入 ISP 的光猫,拨号上网
- 作为默认网关,成为家里所有设备的默认网络出口
- 支持 dhcp 和 dns 服务,可以为家里的其他设备分配 ip 设置默认 dns
当然,用这个东西而不用自己买的路由器有如下两个好处:
- 通常这个东西的性能会更好,在设备很多的时候也不至于出现性能问题,成为网络瓶颈
- 大部分人用这个东西都是为了在这台设备上安装一些代理,然后所有的内网的设备就可以访问各种网站了,这样就省的每个设备都设置代理了,毕竟每个设备各种操作系统设置代理也很麻烦的,尤其是有些设备在安装阶段都需要链接外网,根本没有机会在本机设置代理
不过这并不代表原来的路由器可以扔了,毕竟 ARS2 不是个无线路由器,无法支持 wifi 的,原来的路由器还是要当 AP 继续发挥作用的。
为什么作为旁路由
不过直接把这种软路由做成主路由器有三个问题:
- 原来的路由器要修改成 AP 模式,还要额外的设置...麻烦
- 这台机器其实还有其他的功能,比如可以安装点乱七八糟的插件把它做成个小 NAS,那如果稍有不慎把它搞坏了,那全屋子的网就没了
- 这个东西主要是作为代理用的,但众所周知现在的代理由于种种原因都没有那么稳定,且配置那种规则也有一定风险,让所有的设备都翻墙其实也夹带着让所有设备都断网的风险,尤其是如果家里的网络使用者很多,且不是所有人都有使用代理的需求,全屋过代理出力不讨好
所以做成旁路由,不开通 DHCP 只是支持流量转发和 DNS 服务即可,这样子全屋设备默认依然连接主路由器,即使软路由玩坏了也不耽误其他设备正常使用,需要翻墙的设备主动修改默认网关到软路由就可以了。
怎么设置
官方有文档和视频教程 https://doc.linkease.com/zh/guide/easepi/common.html#%E6%97%81%E8%B7%AF%E7%94%B1%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F 按照这个设置就可以了。
怎么修改默认网关
这里就以 mac 为例做个记录:
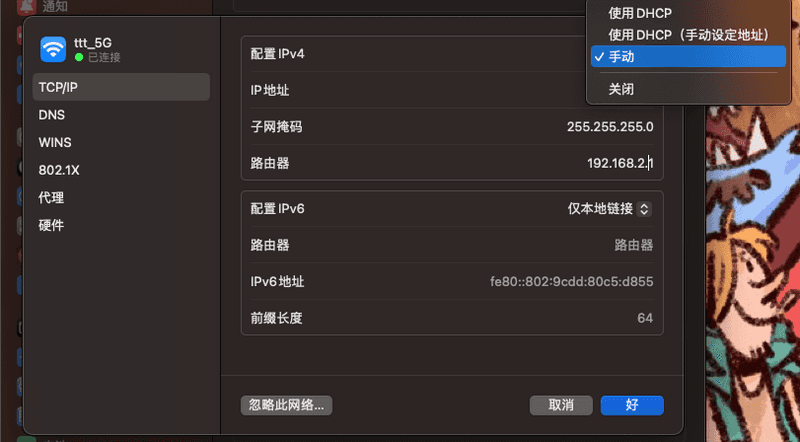
「配置 IPV4」选择为「手动」,然后「路由器」更改为软路由的 IP。
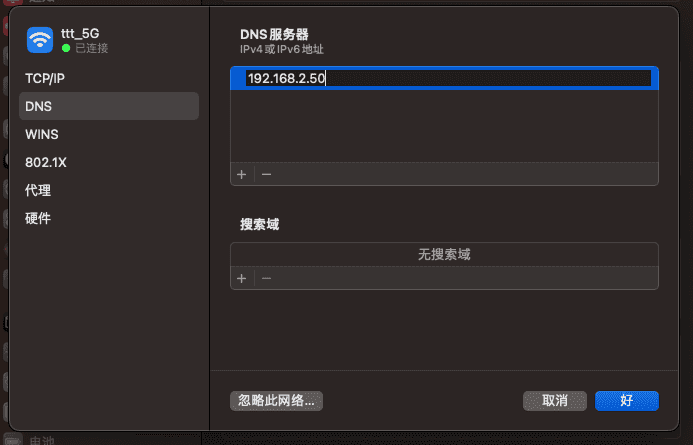
点击左侧的「DNS」把这里的 DNS 服务器也修改成软路由的 IP。
目前我的 truenas scale 就修改了默认网关指向了软路由,这样可以让 truenas scale 里的 k3s 无需额外的设置就能拉到各种镜像了,非常的省心。但如果是笔记本之类的便携设备,这么做会导致你在更换设备使用的地方后无法上网(别问我怎么知道的),一定要记得切换回来。
使用 ansible 的 facts 生成 hosts 信息
2022 December-06
最近在看以前的代码,发现 ansible 的代码里有一些模板是从 ansible 的 vars 生成 /etc/hsots 的代码。这里做了些调研,了解了下用法。这里大量的过程都放到了视频里了,下面的算是笔记吧。
facts 是什么,如何收集
facts 可以理解为 ansible 从主机收集的各种信息,通过如下命令可以看其到底收集了什么:
ansible all -i inventory.yaml -m gather_facts通过 ansible-doc gather_facts 可以知道这个行为是在 playbook 执行之处就自动执行的。
如何使用 facts 生成 hosts 文件
ansible 帮我们收集的 facts 会放进 vars 里供我们使用。比如 hostvars 这个变量里就有了 facts 的信息,可以通过 debug 来展示这个信息:
- hosts: "all"
tasks:
- name: Debug hostvars
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: hostvars- hosts: "all"
tasks:
- name: Debug groups
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: groups执行命令 ansible-playbook all -i inventory.yaml generate_hosts.yaml 可以看到其中的内容。
然后这里我提供一个简单的模板文件 hosts.j2:
{% for host in groups["all"] | sort -%}
{% if hostvars[host]['ansible_default_ipv4'] is defined -%}
{{ hostvars[host]['ansible_default_ipv4']['address'] }} {{ hostvars[host].hostname }}
{%- endif %}
{% endfor %}利用如下的 playbook 就可以生成 hosts 文件了(我这里就放到了 home/test 做了个测试,没有实际覆盖 /etc/hosts)。
- hosts: "all"
tasks:
- name: Test hosts
ansible.builtin.blockinfile:
path: /home/ubuntu/test
marker: "# -----{mark} NODES IN CLUSTER-----"
create: true
block: "{{ lookup('template', 'templates/hosts.j2') }}"补充 inventory.yaml
virtualmachines:
vars:
ansible_user: ubuntu
hosts:
vm01:
ansible_host: 106.75.236.174
hostname: vm01
vm02:
ansible_host: 113.31.107.13
hostname: vm02可以看到这里给每个 vm 配了一个 hostname 然后在 hostvars 里也能拿到的。